What is Display Screen Equipment (DSE)?
Display Screen Equipment (DSE) refers to the various screen-based devices used for work tasks across modern workplaces.
As technology continues to shape how we work, the level of time spent using digital tools has increased substantially. Understanding what counts as DSE helps organisations identify risks and ensure that appropriate safety measures are in place.
DSE can be found in offices, homes, vehicles, and mobile working environments, making it relevant to a wide range of job roles.

Lady Justice symbolising fairness and legal responsibility — a fitting reminder when asking, “Is DSE a legal requirement?”
Definition of DSE (monitors, laptops, tablets etc)
Display Screen Equipment includes a broad range of electronic devices that require visual interaction or data input.
These devices are used for tasks such as communication, administrative work, data processing, customer service, and remote collaboration.
The term covers both traditional desktop setups and newer portable devices, reflecting the diverse ways in which people now work.
- Desktop computers and monitors
- Laptops, tablets and hybrid devices
- Smartphones used for work
- Touchscreen consoles and kiosks
- In-vehicle display systems
- Multi-screen and adjustable monitor setups
These devices require workers to maintain sustained visual focus or repetitive hand movements, which is why they fall under DSE regulations.
When used for long periods, they can pose ergonomic risks if not properly assessed.
What counts as “use of DSE” in a work context
Use of DSE in a work context generally means interacting with screen-based equipment for job-related tasks.
This can involve anything from data entry and online communication to digital design and virtual meetings.
The Health and Safety Executive (HSE) typically considers a worker a DSE user if they spend continuous or near-continuous periods using screen equipment on a daily basis.
- Emailing and digital communication
- Online research or data review
- Virtual meetings and video calls
- Software-based tasks such as coding or design
- Customer service through live chat systems
- Admin, finance or CRM system use
These tasks often require sustained concentration, minimal movement, and repetitive input.
This is why employers must assess and manage risks for anyone who carries out these activities as a significant part of their job.
The Legal Framework in the UK
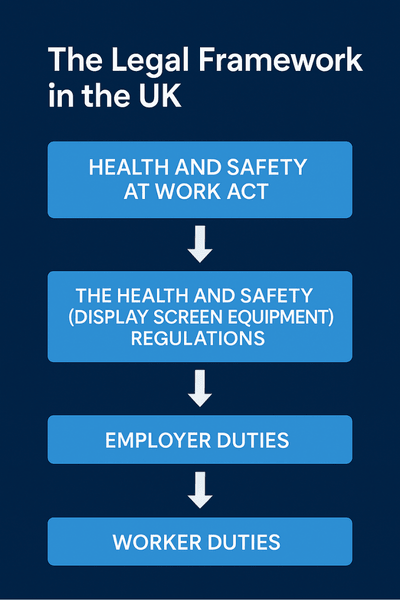
Flowchart showing how UK DSE law is structured, from the Health and Safety at Work Act down to employer and worker duties.
The UK has specific legislation in place to ensure that anyone who works with DSE can do so safely.
These laws help reduce the risk of musculoskeletal problems, eye strain and long-term health issues from poor workstation design.
Understanding the legal framework ensures that employers and employees know their responsibilities and rights.
The Health and Safety (Display Screen Equipment) Regulations 1992 (and amendments)
The DSE Regulations 1992 set out the minimum requirements for safe workstation use. They cover workstation layout, equipment suitability, rest breaks, training and eye care.
These regulations ensure that all workers using screen-based equipment have a safe and comfortable working setup.
- Employers must assess DSE risks
- Workstations must meet ergonomic standards
- Regular breaks or changes of activity are required
- Eye tests must be available to DSE users
- Training and information must be provided
These rules apply to office workers, home-based staff, hybrid workers and mobile employees, helping to reduce preventable issues associated with prolonged screen use.
How this fits with the Health and Safety at Work etc. Act 1974
The DSE Regulations sit under the wider Health and Safety at Work etc. Act 1974, which places a general duty on employers to ensure the health, safety and welfare of employees.
The act requires employers to take reasonable steps to manage risks, provide safe equipment, and ensure that workers understand how to carry out their job safely.
- Employers must create a safe working environment
- Risks must be identified, reviewed and reduced
- Equipment must be suitable and properly maintained
- Workers must be given appropriate training
Carrying out DSE assessments forms part of an employer’s legal duty to protect workers, ensuring that risks linked to screen use are managed effectively.
What the key obligations are (employers, workers)
Both employers and employees have responsibilities under DSE legislation. Employers must put systems in place to protect workers, while employees must follow guidance and use equipment correctly.
- Employers must carry out DSE assessments
- Employers must provide suitable equipment
- Employees must use equipment as trained
- Employees must report discomfort or workstation issues
- Employers must offer training and eye tests
Together, these shared responsibilities help maintain a safe working environment and reduce the risk of long-term health problems.
When Does the DSE Legislation Apply?
DSE legislation applies when workers regularly use screen-based equipment as part of their daily duties.
Employers must understand when the regulations apply so they can implement the correct safety measures.
Who is considered a “DSE user” (daily, 1 hour+ etc)

Daily screen work for an hour or more meets the HSE definition of a DSE user.
The HSE considers workers to be DSE users if they use screens for an hour or more at a time, on a regular basis.
These individuals are most at risk of issues such as eye strain and musculoskeletal discomfort.
- Office workers who use screens throughout the day
- Remote workers relying on digital tools
- Hybrid staff switching between home and office
- Data entry and administrative employees
- Customer service staff using digital systems
Identifying DSE users helps employers determine who needs a formal DSE assessment and ongoing monitoring.
What kinds of workstations / situations are covered (office, home working, hot-desking)
DSE regulations apply to a wide range of working environments. Whether someone works at a fixed office desk, uses shared spaces or works remotely, employers must ensure that their workstation is safe and ergonomically sound.
- Office-based workstations
- Home-working setups
- Hot-desking environments
- Co-working spaces
- Mobile and vehicle-based workstations
Each situation presents different ergonomic risks, which must be reviewed and managed to ensure safe screen use.
When the legislation does not apply (occasional or short use)
DSE legislation does not apply to workers who only use screen equipment occasionally or for short periods that do not amount to daily, prolonged screen work
In these cases, the risk of long-term strain is much lower.
- Occasional screen use
- Short, infrequent tasks
- Roles not requiring daily digital input
- Minimal interaction with computer systems
Even though the regulations may not apply formally, general good ergonomic practice is still recommended for anyone using screens at work.
What Are the Main Duties Under DSE Regulations?
DSE regulations outline specific duties for employers and employees to ensure that screen-based work is carried out safely. These responsibilities help reduce the risk of discomfort and injury.
Duty on employers (risk assessments, workstation setup, training, eye tests)

Key employer responsibilities under DSE law, including assessments, training and ergonomic support.
Employers have a legal duty to assess DSE risks and take steps to protect workers. This includes ensuring that equipment is appropriate, training is provided and eye tests are available.
- Carrying out formal DSE assessments
- Providing ergonomic equipment
- Offering training on safe screen use
- Providing free eye tests on request
- Making reasonable adjustments for worker comfort
These measures ensure safe and comfortable working conditions for DSE users.
Duty on employees / users (correct use, taking breaks, reporting issues)
Employees also have responsibilities under the regulations. They must use equipment as instructed, take regular breaks and report any issues that could affect their wellbeing.
- Following ergonomic training
- Adjusting equipment correctly
- Taking breaks from screen use
- Reporting discomfort or faulty equipment
By following these steps, employees help to protect themselves from preventable health issues.
Shared responsibilities (home working, hybrid setups)
In home-working and hybrid arrangements, both employers and workers must play an active role in setting up a safe workstation.
Effective communication ensures that risks are managed regardless of where work takes place.
- Employers provide guidance and equipment
- Employees set up their home workstation safely
- Both parties review risks regularly
- Adjustments are made when circumstances change
This shared approach maintains safety standards across all working environments.
Is DSE a Legal Requirement?
DSE assessments are the recognised method for meeting legal duties under DSE regulations. Understanding how these requirements work helps organisations ensure compliance and protect their workforce.

A professional worker seeking clarity on DSE requirements in a modern digital workplace.
Clarifying “legal requirement” – what must be done under law
While the law does not explicitly require a “DSE assessment” by name, employers are legally required to assess and manage DSE-related risks.
Completing a DSE assessment is the accepted and expected way of fulfilling this obligation.
- Employers must identify DSE risks
- Assessments must be completed for DSE users
- Records should be kept, especially with 5+ employees
- Risks must be reduced or eliminated
In practice, this means that a DSE assessment is essential to demonstrate compliance.
Risks of non-compliance (enforcement, employee claims, health risks)
Failing to comply with DSE regulations can lead to legal and financial consequences. Non-compliance increases the risk of workplace injuries and may result in enforcement action or employee claims.
- Enforcement notices or penalties
- Compensation claims for workplace injury
- Increased sick leave and productivity loss
- Long-term health risks for employees
Managing DSE risks helps protect both workers and the organisation.
Misconceptions / common misunderstandings
There are several common misunderstandings about DSE regulations, which can lead to poor compliance.
- “DSE rules only apply to office workers”
- “Home workers don’t need assessments”
- “A simple online checklist is enough”
- “Short breaks aren’t necessary”
Clarifying these misconceptions helps ensure that workers receive appropriate support.
Practical Advice for Workers and Employers
Both workers and employers can take simple steps to reduce risks related to screen use. Good practice helps improve comfort, productivity and wellbeing.
What workers can do (check their workstation, ask for assessment, take breaks)

A clear guide to healthy DSE habits, highlighting what to do—and what to avoid—to maintain safe and comfortable screen use.
Workers can take proactive steps to ensure their workstation is comfortable and safe.
- Adjust chairs and screens properly
- Request a DSE assessment if needed
- Take regular breaks from screen work
- Report any discomfort early
These habits help prevent discomfort and long-term health issues.
What employers should do (carry out assessments, write records, review when changes)
Employers should take structured steps to ensure compliance and maintain safe working conditions.
- Complete DSE assessments for users
- Keep accurate records of assessments
- Review setups when equipment or roles change
- Provide training and suitable equipment
These actions help employers meet their legal responsibilities.
Special situations: home working, hot-desking, mobile workers
Different working environments create different risks. Employers and workers should take extra care in non-traditional workspaces.
- Provide portable equipment for home or mobile workers
- Ensure hot-desking setups can be adjusted easily
- Review lighting and seating in home offices
- Assess mobile workers’ screen use
Taking these steps helps reduce risks across all working arrangements.
A modern workstation displaying detailed analytics dashboards, typical of roles involving regular DSE use.
Summary and Key Takeaways
DSE regulations play an essential role in protecting workers from preventable health issues related to screen use.
By understanding and applying these requirements, employers and employees can create healthier, safer and more productive working environments.
Recap of legal obligations
- Employers must assess and manage DSE risks
- DSE users must have safe, ergonomic workstations
- Eye tests and training must be provided
- Records should be kept and reviewed regularly
These obligations apply in offices, home-working setups and hybrid environments.
Why it matters for health and productivity
Good DSE practice helps prevent discomfort, reduce fatigue and support long-term wellbeing.
A well-designed workstation can significantly improve concentration, performance and job satisfaction.
Going forward – good practice beyond legal minimum
While legal compliance is essential, going beyond the minimum requirements can enhance comfort and productivity. Regular reviews, ergonomic equipment and open communication all contribute to healthier working habits.